A staggering 78% of businesses across the world experienced an increase in the volume of cyberattacks because of a shift towards remote working – according to recently released data by Atlas VPN.
Even though social media platforms are flooded with news of companies proudly presenting the fact that they are permanently shifting to a remote-work environment, they usually do not mention the fact that the pivot has created major issues for their security.
Unpatched personal devices, erratic employee behaviour, and inadequately protected home networks create many loopholes for threat actors to exploit.
In June 2021, Carbon Black, a company that provides workload protection services, surveyed 3,542 CIOs, CTOs, and CISOs from various industries and 14 different countries to uncover if WFH (work from home) resulted in an increase in cyberattacks.
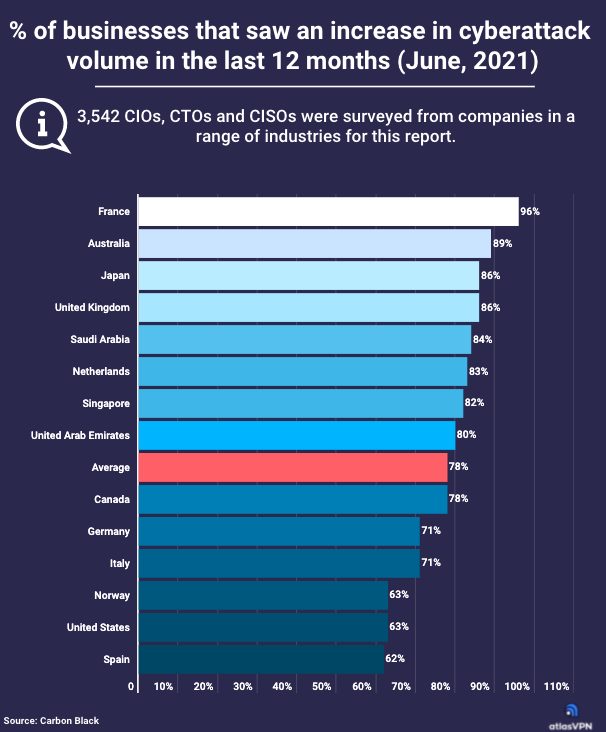
The study shows that a whopping 96% of enterprises in France saw a significant increase in the number of attacks due to the shift to a WFH environment.
The second most affected country is Australia, where 89% of cybersecurity professionals reported that attacks increased due to employees working remotely. The United Kingdom and Japan share third and fourth place, with 86% of respondents stating that they noticed a significant jump in cyber threats in the past year.
As many as 84% of businesses in Saudi Arabia, 83% in the Netherlands, 82% in Singapore, and 80% in the United Arab Emirates said that attacks jumped substantially. Canada is in line with the global average, where 78% of enterprises reported a growth in the cyberattack volume.
Interestingly, the United States is at the lower side of the scale, with 63% of cybersecurity professionals reporting an increase in cyber threats in the past year.
In addition, 79% of respondents noticed that attacks had become more sophisticated. Meaning, hackers are willing to spend more time creating targeted attacks. These attacks aim to disarm specific security measures the target company has in place.
Perhaps even more shocking is the fact that the companies that had a cyberattack reported having an average of 2.35 breaches per year. These were not minor leaks either. In 80% of the breaches, the incident was material, which means that it was significant and was reported to regulators or the incident response (IR) team.
This data is in line with earlier reports, which highlighted how over 5 billion personal records were leaked in Q1 of 2021, whilst 37 billion data records leaked in 2020, a growth of 140% year-over-year.




